By Abimbola Ogunnaike
In an effort of bolstering the fight against one of the most deadly infectious diseases globally, the world’s biggest vaccine maker ,Serum Institute of India (SII), has announced that it will start rolling out a cheap new malaria inoculation in Africa in May,
The mosquito-borne malady kills more than 600,000 people a year, 95 per cent of them in Africa, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
It is more fatal among the young, and the annual toll of malaria deaths includes nearly half a million African children aged under five.
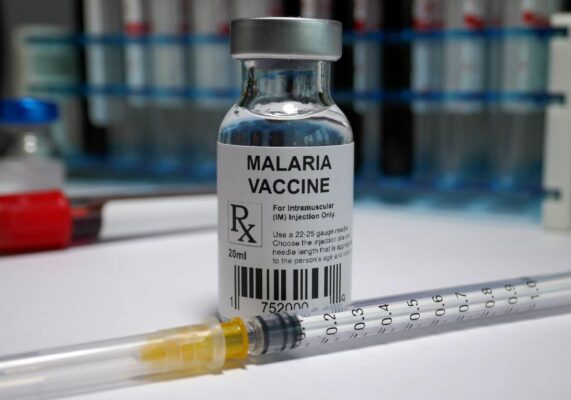
The Serum Institute of India (SII) this year plans to ship 25 million doses of the new vaccine, developed along with Oxford University researchers and known as R21.
“In terms of importance and saving lives… it’s going to be a hugely impactful vaccine, SII chief executive Adar Poonawalla told AFP.
“We’ve offered these vaccines to the African continent at $4 or less in the first year itself. And then as we scale up, maybe we can bring that down a little bit further.”
The R21 vaccine, a three-dose course and booster shot for children aged 5-36 months is the second malaria shot approved by the WHO.
However, researchers say it will be cheaper than the other vaccine produced by British pharma giant GlaxoSmithKline.
The WHO said its rollout was expected to greatly expand supply to meet high demand from African countries.
The SII has been the largest vaccine manufacturer globally for several years but saw its profile rise substantially after manufacturing millions of cheap COVID-19 vaccine shots for export at the height of the pandemic.
With demand for coronavirus prevention waning, it has repurposed some pandemic-era facilities to combat other diseases at its sprawling factory complex in Pune, a few hours’ drive from business capital Mumbai.
Small glass vials are pumped with R21 doses and whizzed off on a conveyor belt for quality checks and packaging ahead of their looming export.
Poonawalla says the institute’s goal is to roll out R21 in a few countries before the main malaria season starts in about six to seven months.
“Ideally we should have vaccinated the people most vulnerable at risk. That’s the target,” he said, adding that production would eventually reach 100 million R21 doses per year.
SII research and development director Umesh Shaligram said the vaccines would be shipped towards the end of April with deployment to start by May and June.
The vaccines will mostly be bought and distributed through the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) and Gavi, a global vaccine alliance.
Chad, Central African Republic, DR Congo, Mozambique and South Sudan will be the first five countries to receive R21 doses, a UNICEF spokesperson told AFP.
“Uganda and Nigeria are planning to introduce it later in the year,” the spokesperson added.